SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) is a multi-dimensional OLAP server as well as an analytics engine that allows you to slice and dice large volumes of data. It is part of Microsoft SQL Server and helps perform analysis using various dimensions. It has 2 variants Multidimensional and Tabular. The SSAS full form is SQL Server Analysis Services.
First in this SSAS tutorial, we will learn about the SSAS architecture:

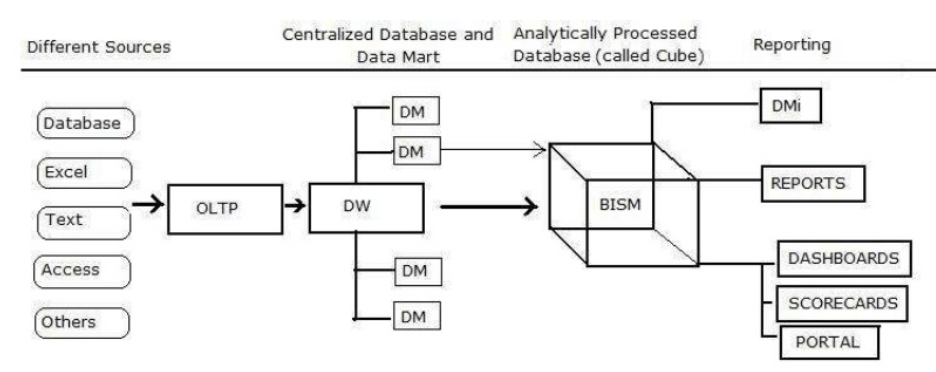
The architectural view of SQL server analysis services is based on a three-tier architecture, which consists of
Now in this SSAS tutorial, we will go through the history of SSAS:
Now in this SSAS tabular model tutorial, we will learn some important terminologies of SSAS:
Data Source is a kind of connection string. It establishes a connection between the analysis database and RDBMS.
Data source view is a logical model of Database
A cube is a basic unit of storage. It is a collection of data which has been aggregated to allow queries to return data quickly.
The MOLAP is made of data cube which contains of measures and dimensions. It includes all the members who may be in a hierarchical relationship.
It is specific set of rule which helps you to determine how certain cells are computed in a sparse cube and measures values rolled up inside that hierarchies.
Dimension offers the context surrounding a business process event. In simple terms, they give who, what, where of a fact. In the Sales business process, for the fact sales number, dimensions would be who customer Names.
Each type of summary which can be retrieved from the single dimension is called label.
A fact table is the most important table in a dimensional model. A Fact Table contains Measurements/fact and Foreign key to the dimension table. For example, payroll operations.
Each fact table contains one or more table which should be analyzed. For example, a book sells information table. It can be a profit or loss for the number of book’s sold.
The database schema of a database system and its structure described in a formal language. It supports the database management system. The term “schema” means to the organization of data as a blueprint of a manner of which database is constructed.
Now, we will learn types of models in SSAS in this SSAS cube tutorial:
The Multi-Dimensional Data Model, which consists of a data cube. It is a group of operations which allows you to query the value of cells by using cube and dimension members as coordinates.
It defines rules which decide the way that measure values are rolled up within hierarchies or how specific values are computed in a sparse cube.
Tabular modeling organizes data into related tables. The table doesn’t designate as “dimensions” or “facts” and development time is less with tabular because of all related tables able to serve both roles.
| Parameters | Tabular | Multidimensional |
|---|---|---|
| Memory | In memory cache | File-based storage |
| Structure | Loose structure | Rigid structure |
| Best feature | Data does not need to move from source | It is best when data is put into a star schema. |
| Type of Model | Relational model | Dimensional model |
| DAX | MDX | |
| Complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Size | Smaller | Larger |
Essential features of SSAS are :
| Parameter | SSAS | PowerPivot |
|---|---|---|
| What is | SSAS Multidimensional is “Corporate BI” | Microsoft PowerPivot is a “Self- Service BI |
| Deployment | Deploy to SSAS | It is deployed to SharePoint |
| Use for | Visual Studio Project | Excel |
| Size | Size limited to memory | Capacity limited to 2 GB. |
| Partition support | Supports Partitioning | No partitions |
| Query type | DirectQuery and Vertipaq | Allows only Vertipaq Queries |
| Admin tools | Server Admin tools (e.g., SSMS] | Excel and SharePoint “Admin” |
| Security | Row-level & dynamic security | Workbook file security |
Pros/benefits of SSAS are: